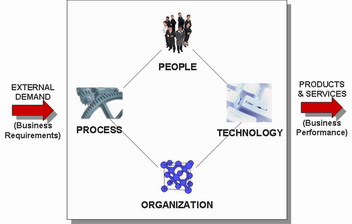
Source / Reference:
1. A. Albadvi (2003), "Customer Relationship Management (CRM)"
2. El Sawy's Redesign Principles and Tactics (2001)
3. M&M
=================================================================================
To have a more viable process redesign, principles and tactics can be used as a checklist for suggesting ways of process redesign as well as triggering ideas for change implementation so as to maximize the value adding. There are 3 types of redesign principles as shown as below, the first 2 types are introduced in this lecture.
Principle #0 : Streamline
Principle :
Removing waste, simplify and consolidate similar activities.
Removing waste, simplify and consolidate similar activities.
Tactics :
1. Reducing complexities
2. Eliminating unnecessary activities (e.g. paperwork and other repetitive tasks)
1. Reducing complexities
2. Eliminating unnecessary activities (e.g. paperwork and other repetitive tasks)
Example :

McDonald offers real time / just-in-time food production, is one of the example. It produces the food instantly when customer order arrived. Waste of products can be avoided. Meanwhile, the food ordering business processes can be simplified using the computerized system and screen display.

McDonald offers real time / just-in-time food production, is one of the example. It produces the food instantly when customer order arrived. Waste of products can be avoided. Meanwhile, the food ordering business processes can be simplified using the computerized system and screen display.
Restructuring process
Principle #1 : Lose Wait
Principle :
Reducing waiting time in process to create value
Tactics :
1. Turning time-sequential activities into concurrent execution
2. Creating closed-loop teams
3. Not allowing a support activity to gate a core value-adding process
4. Designing for continuous flow / real time processing instead of batching processing
5. Modifying upstream practice to relieve downstream bottleneck
Example :
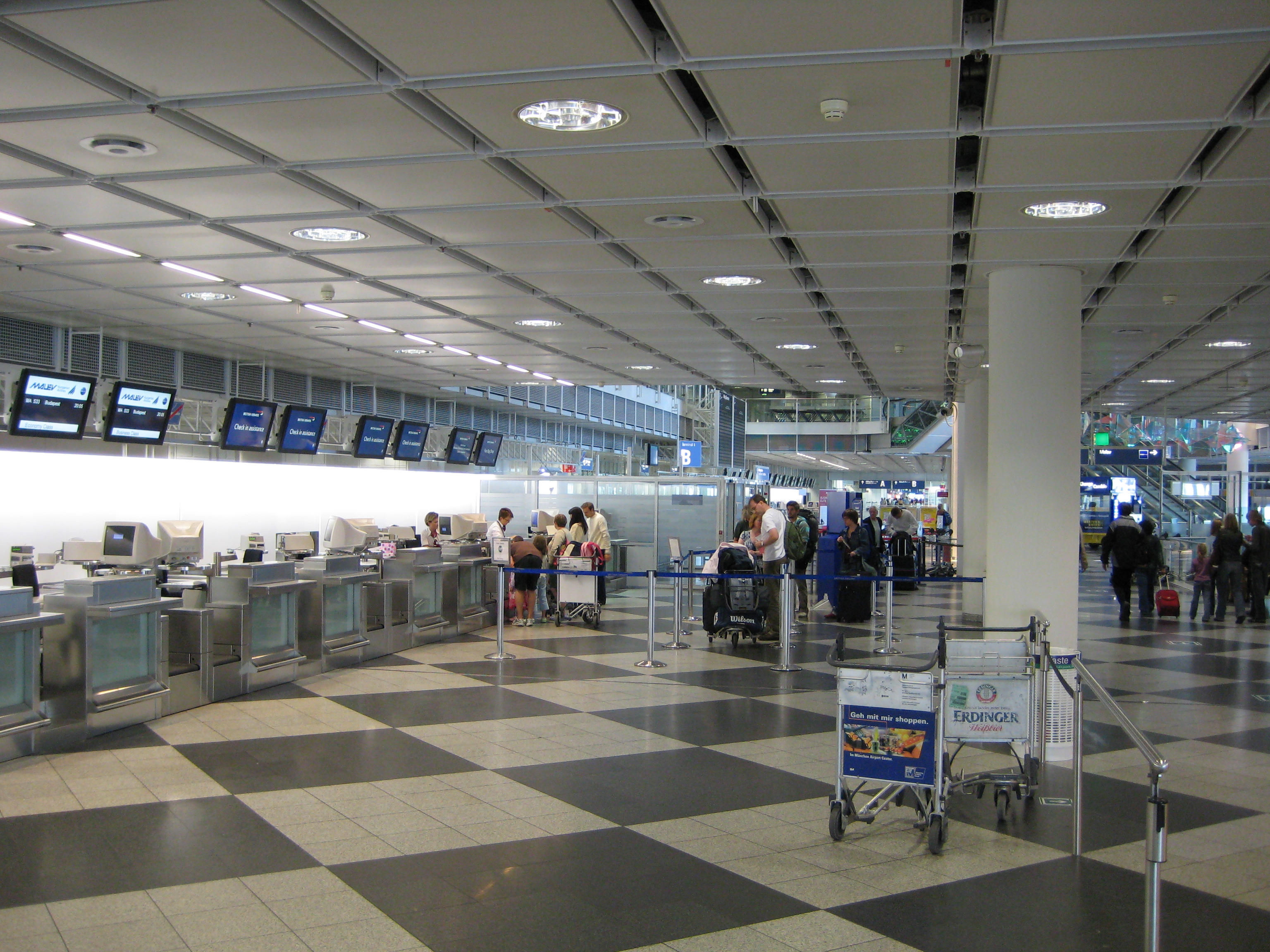


The check in process of the airport industry can illustrate the "concurrency". Several counters are opened for segmenting different types of travelers, operating in parallel. Efficiency can be enhanced. The waiting and cycle time can also be greatly reduced. The banking sector (e.g. HSBC) and travelling agency are another example.
Principle #2 : Orchestrate
Principle :
Let the swiftest and most able enterprise execute
Tactics:
1. Partnering
2. Outsourcing
3. In-sourcing
4. Routing through an intermediary
Example :
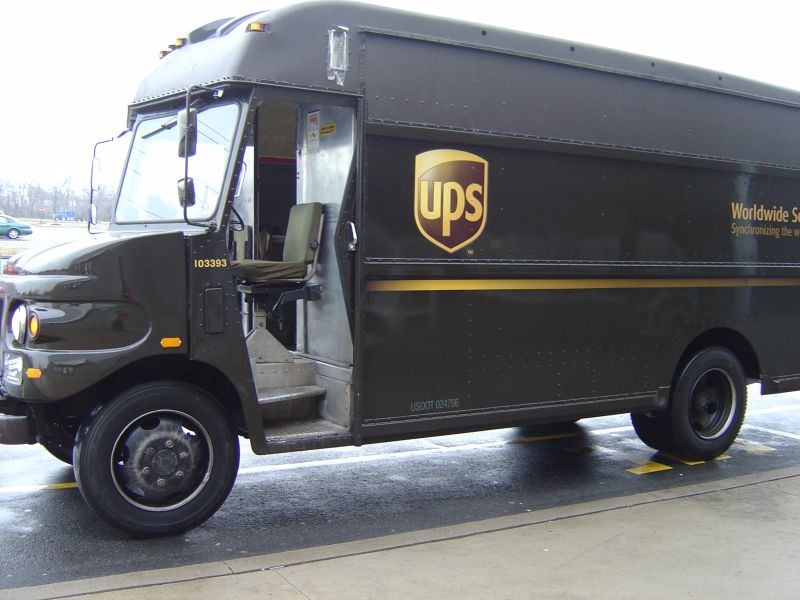


To demonstrate the "in-sourcing", United Parcel Service (UPS) is an good example. As TOSHIBA was criticized for long time delay in repair pickup and fixed product delivery, it has in-sourced the maintenance and repairs logistics process to UPS. Both parties gain from the in-sourcing. For TOSHIBA, its service time is shortened. Its reputation is gradually improved as well. For UPS, its transportation time and cost are reduced. Moreover, since maintenance skills is an emphasis of the in-sourcing, it equips the workers with more knowledge on this aspect, thus enhancing the company diversity.


For outsourcing, more offices in the commercial industry prefer to outsource the cleaning process to some specialized cleaning company. Another cleaning process outsourcing example is the KMB. Since cleaning is definitely not the core competence of these business, outsourcing can reduce the cost, improve the flexibility as well as process efficiency.
Principle #3 : Mass-customize
Principle :
Flexing the process in terms of time, place and way.
Tactics :
1. Expanding time window for the process
2. Creating more physical space options
3. Creating modular process platforms
4. Pushing customization to occur closest to the customer
5. Offering dynamic customization
Example :

The service "Create Yours" offered by the M&M company is a good example illustrating this principle. Apart from the standardized packaged chocolates, the customers can create their unique set of chocolates for different purpose and occasions (e.g. birthday, wedding, etc.) Customers can choose to customize the color, image and packaging according to their preference. "Dynamic customization" is achieved under the adoption of "build-to-order". Upon M&M received the online order, the M&M chocolate with specific customized pattern will be produced.
Here is one of the example of designing chocolates for marriage proposal. Apart from selecting picture from clip-art, customers can even choose to import their own picture or write message over the chocolate.
Below are the steps of my trial for making my own chocolate. (It is really user-friendly with just few simple clicks!)
 After that, customers can then choose to "add to cart" and select the payment and delivery method.With the use of the effective online store and design platform, the tactics "flexing time" and "flexing space" can also be realized. Since the webpage is on 24-hour operation with location independence, the temporal and spatial limitation can be eliminated. It can enhance the accessibility as well as convenience of the service and facilitate transaction.
After that, customers can then choose to "add to cart" and select the payment and delivery method.With the use of the effective online store and design platform, the tactics "flexing time" and "flexing space" can also be realized. Since the webpage is on 24-hour operation with location independence, the temporal and spatial limitation can be eliminated. It can enhance the accessibility as well as convenience of the service and facilitate transaction.  Dell is another example reflecting the usage of this principle. its online ordering system enable customers to select components (e.g. processor, operating system, media storage device, etc.) of its product, which provides customers with convenient and customized online shopping experience.
Dell is another example reflecting the usage of this principle. its online ordering system enable customers to select components (e.g. processor, operating system, media storage device, etc.) of its product, which provides customers with convenient and customized online shopping experience.Below is an example of an online order with various components selection.http://configure.us.dell.com/dellstore/config.aspx?oc=bpctmsaio&c=us&l=en&s=bsd&cs=04&model_id=optiplex-390
Principle #4 : SynchronizePrinciple:Synchronizing the physical & virtual parts of the process.Tactics:
1. Matching physical & virtual parts of the process offerings 2. Creating common process platforms
3. Tracking physical products movement electronically Example:
 The online store ebay is a successful example illustrating the tactic "product movement tracking". After checking out, an email containing tracking information of the product will be received. It can be used for checking the shipping status of the items purchased on the shipping company's website.
The online store ebay is a successful example illustrating the tactic "product movement tracking". After checking out, an email containing tracking information of the product will be received. It can be used for checking the shipping status of the items purchased on the shipping company's website.Changing information flows around processes
Principle #5 : Digitize and PropagatePrinciple:
Capture information digitally at the source & propagate it throughout the process.Tactics:
1. Shifting data entry to customers and digitizing it
2. Making process paperless
3. Making information more easily accessible upstream & downstream
4. Shrinking the distance between information & decisionExample:
 Fortress is another online store which can show the application of this principle. With the use of online ordering, self-service is enabled where customers have to register, enter personal information and review online catalogue on their own. In other word, the data entry is shifted to the customer. On the other and, the information collected will be automatically entered into the database and transferred to other department for later processing. Since centralized computer system and database are used, information can be directly accessible and retrievable online. The digitization can enhance the efficiency of the transaction processing and reduce the possible human error, leading to improved customer satisfaction and profitability.Principle #6 : VitrifyPrinciple:
Fortress is another online store which can show the application of this principle. With the use of online ordering, self-service is enabled where customers have to register, enter personal information and review online catalogue on their own. In other word, the data entry is shifted to the customer. On the other and, the information collected will be automatically entered into the database and transferred to other department for later processing. Since centralized computer system and database are used, information can be directly accessible and retrievable online. The digitization can enhance the efficiency of the transaction processing and reduce the possible human error, leading to improved customer satisfaction and profitability.Principle #6 : VitrifyPrinciple:Provide glass-like visibility through fresher & richer information about process status.Tactics:
1. Providing on-demand information tracking
2. Providing reporting capabilities with on-the-fly analysis
3. Designing standard partner interface Example:
 FedEx is a shipping company which offers a tracking system for customer to track their package delivery. In this case, the transparency of the shipping process increases, leading to the improvement of the reliability and customer loyalty.Principle #7 : SensitizePrinciple:
FedEx is a shipping company which offers a tracking system for customer to track their package delivery. In this case, the transparency of the shipping process increases, leading to the improvement of the reliability and customer loyalty.Principle #7 : SensitizePrinciple:Fit the process with sensors & feedback loops to prompt actionTactics:
1. Building in customer feedback loops to detect process dysfunction
2. Enabling software smarts to trigger quick business reflexes
3. Attaching environmental probes to the process to monitor changeExample:
 Walmart is a multinational supermarket which offers superior online purchasing service. To maintain the smooth operation of the business, Walmart takes significant consideration on customer satisfaction. It provides a feedback e-form which is easily accessible on its webpage. Customers' opinion towards the online ordering system is encouraged. It aims at providing customers with high quality online shopping experience.
Walmart is a multinational supermarket which offers superior online purchasing service. To maintain the smooth operation of the business, Walmart takes significant consideration on customer satisfaction. It provides a feedback e-form which is easily accessible on its webpage. Customers' opinion towards the online ordering system is encouraged. It aims at providing customers with high quality online shopping experience.